Control and Coordination Class 10
CBSE Science Notes biology Chapter 7
➣ Coordination-The working together of various organs of the body of an organism in a proper manner to produce appropriate reaction to a stimulus is called coordination.
➣ Stimulus- The changes in the environment to which an organism responds and reacts is called Stimulus
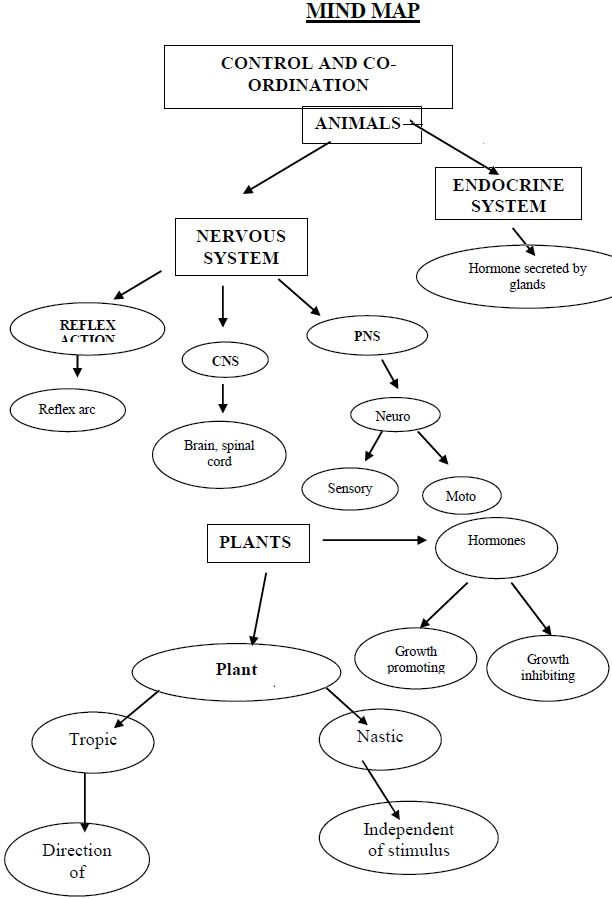
➣ Control & coordination in animals- takes place by (i) Nervous system & (ii) Endocrine system
➣ Nervous system
Stimulus → Receptor organ → Sensory nerve → Brain/Spinal cord
↓ Response ← Effector organ ← Motor nerve
➣ Endocrine system
Stimulus → Endocrine organ → Secrete hormone → Hormone in blood ↓
Response ← Target organ
➣ Parts of the Nervous system –
(i) Brain (ii) Spinal cord (iii) Nerves (Neurons)
➣ A Neuron is the structural & functional unit of Nervous system
➣ Parts of a neuron-
(i) Dendrites (ii) Cell body (iii) Axon
➣ Synapse- Space/junction between two adjacent nerves is called Synapse.
➣ Passing of information takes place –
(i) By Electric impulse (inside the neuron) and
(ii) In the form of chemicals (At synapse)
➣ Reflex action- Spontaneous, involuntary and automatic response to a stimulus to protect us from harmful situations. Eg. On touching a hot object unknowingly we instantly withdraw our hand.
➣ Reflex arc- The pathway of the reflex action is called Reflex arc.
Stimulus → Receptor organ → Sensory nerve → Spinal cord →Effector organ→ Response
Refer to figure 7.2 page no. 117 of N.C.E.R.T Text book)
➣ Nervous system-
(1) Central Nervous system (CNS)
(2) Peripheral Nervous system(PNS)
(i) Brain (i) Autonomic Nervous system
(ii) Spinal cord (ii) Voluntary Nervous system
➣ Brain
(i) Centre of coordination of all activities
(ii) Thinking is involved
(iii) Complex process
➣ Parts of brain-
Refer to figure 7.3 page no. 118 of N.C.E.R.T Text book
Fore brain | Mid brain | Hind brain |
(i) Cerebrum |
---------- | (i) Cerebellum |
➣ Fore brain Cerebrum-
(i) Main thinking and largest part of the brain.
(ii) It has 3 main areas-
a) Sensory area- to receive impulses from sense organs via Receptors
b ) Motor area- control voluntary movements.
c) Association areas- Reasoning, learning & intelligence. Thalamus – It relays sensory information to the Cerebrum
Hypothallamus- It forms the link between Nervous system & Endocrine system
➣ Mid brain- It connects Fore brain and Hind brain. Controls reflex of eyes & ears
➣ Hind brain- Connects the Fore brain & Hind brain
Cerebellum – Controls & coordinates muscular movements, maintaining body posture and equilibrium.
Pons- Acts as a bridge between brain & spinal cord
Medulla oblongata- Controls involuntary actions like blood pressure, salivation, vomiting, etc.
➣ Spinal cord- Cylindrical or tubular structure extending downwards from the Medulla oblongata.
➣ Protection of the brain & the spinal cord-
(i) Bony outer covering: skull for the brain & vertebral column for the spinal cord.
(ii) Cerebrospinal fluid present in between the three membranes.
➣ Action caused by Nervous tissue
Information → Nervous tissue → Brain Muscles → Causes action
➣ Path or action-
Nerve impulse → Muscle cell → Changes shape due to special proteins
↓
Action caused ← Shorter form of muscles ← Change shape & arrangement of cell
➣ Chemical communication by hormones- (advantages)
(i) Electrical impulses have their limitations because they reach only those cells connected to the nervous tissue.
(ii) Also the nerve cells cannot generate & transmit impulses continuously.
iii)Electrical communication is slower.
➣ Hormones-
(i) are chemical messengers secreted by endocrine glands
(ii) Are secreted in small amounts & may act in nearby places or distant places.
(iii) Do not take part in the reaction & are destroyed immediately.
➣ Hormones are secreted by- Endocrine glands & Exocrine glands
S. No. | Endocrine glands | Exocrine glands |
1. | Ducts absent | Ducts present |
2. | Secrete hormones | Secrete enzymes |
3. | Secreted in blood | Secreted in ducts of glands |
4. | Situated away from the site of action | Situated near the site of action |
➣ Some glands which act as both endocrine & exocrine
Gland | Endocrine function | Exocrine function |
Pancreas | Produces insulin & Glucagon | Produces digestive enzyme. (pancreatic |
Testes | Produces hormone | Produces male gametes (reproductive cells) |
Ovaries | Produces hormone Oestrogen | Produces female gametes (reproductive |
➣ Important Endocrine glands, the hormone they secrete & their function
Refer to figure 7.7 page no. 124 of N.C.E.R.T Text book)
Endocrine gland | Hormone | Function |
Pituitary gland | Growth hormone | Body growth, development of bones & muscles |
Thyroid gland | Thyroxine | Regulates carbohydrate, protein & fat |
Pancreas | Produces insulin & | Regulates blood sugar levels (if less diabetes is |
Testes in males | Produces hormone | Development of secondary male characters like |
Ovaries in | Produces hormone | Development of secondary female characters like |
➣ Coordination in plants- Only chemical coordination is present in plants.
➣ Tropic movements- The movements of plants in the direction of stimulus (positive) or away from it (negative) are called tropic movements. E.g. Phototropism, Geotropism. Chemotropism.
Refer to figure 7.4 & 7.5 page no. 121 of N.C.E.R.T Text book)
➣ Nastic movements -The movements of plants independent of stimuli are called nastic movements. E.g.- Touch me not plant leaves close when touched.
➣ Plant hormones (Phytohormones) Examples-
1. Auxins- Help in growth of root & shoot tips.
2. Gibberellins- Help in vegetative growth
3. Cytokinins- Promote cell division
4. Abscissic acid - Inhibits growth & causes wilting (falling) of leaves
➣ Important diagrams-
1. Structure of neuron (nerve cell)
2.Reflex arc
3.Human brain
4.Endocrine glands .
1. To compare taste of sugar and food with open & blocked nostrils.
2. To demonstrate the response of a plant to the direction of light. 3. To demonstrate hydrotropism












Welcome to Pdakoo ❣️
Shaping the future of tomorrow!